The air around you contains about 80 percent nitrogen and 20 percent oxygen. If you require the use of portable oxygen to aid with a medical problem then you require a much higher percentage level of oxygen which can be delivered straight to your lungs by portable/at home devices. One such device is an oxygen concentrator.
How They Work:
Your oxygen concentrator takes in air from the surroundings and splits the oxygen from the nitrogen. It then releases the nitrogen back into the surrounding air. The concentrator collects and stores the oxygen and then dispenses it back to the patient.
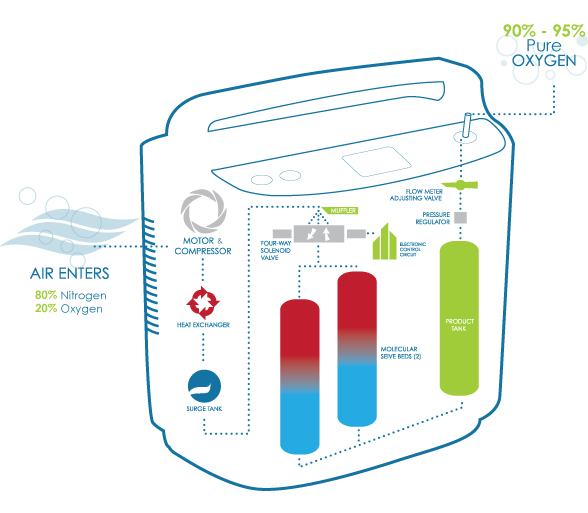
As long as you have it running and set properly, your oxygen concentrator is continually “making” 90 – 95 percent pure oxygen out of normal air, so you’ll have all you need.
Oxygen tanks are already pre-filled with oxygen and have to be re-filled whereas concentrators can make oxygen as it goes. Tanks also run the risk of leakage, which can cause explosions/fires and are heavier and more difficult to move around with.
Concentrators do not pose any danger and the other main benefit is mobility. Most of the concentrators are portable, which means they’re designed to be used at home, on the go and even on a plane, therefore you’ll always have all the oxygen you need, no matter where you are.
Concentrators also have the option of pulse-dose or continuous administration. Pulse-dose is a newer oxygen therapy technology that delivers oxygen through your cannula only when you breathe in. Continuous flow oxygen is constantly flowing through the tubes.
You should talk to your doctor about which dosing method is right for you. Pulse-dose technology can be delivered in a smaller size and will allow for longer battery life. Alternatively, most patients who require oxygen for sleep, use a continuous flow dosage due to shallow night breathing. Sometimes it’s necessary to use continuous flow oxygen while you sleep and pulse-dose oxygen during the daytime.
Reference: http://www.oxygenconcentratorstore.com
1 Comment
Add comment Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.





Thanks for sharing nice information about How portable oxygen concentrators (POC) Works. its very helpful for sleep disordered patients.